ReCreate3D Printing
The printer manufactures airplane parts.
3D Printing – ReCreate3D create physical objects from digital designs.
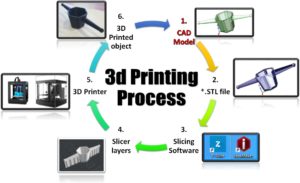
“3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing (AM), refers to processes used to create a three-dimensional object in which layers of material are formed under computer control to create an object. Objects can be of almost any shape or geometry and are produced using digital model data from a 3D model or another electronic data source such as an Additive Manufacturing File (AMF) file. STL is one of the most common file types that 3D printers can read. Thus, unlike material removed from a stock in the conventional machining process, 3D printing or AM builds a three-dimensional object from computer-aided design (CAD) model or AMF file by successively adding material layer by layer.”
- In early 2014, Swedish supercar manufacturer Koenigsegg announced the One:1, a supercar that utilizes many components that were 3D printed.
- Urbee is the name of the first car in the world car mounted using the technology 3D printing (its bodywork and car windows were “printed”).
- In 2014, Local Motors debuted Strati, a functioning vehicle that was entirely 3D Printed using ABS plastic and carbon fiber, except the powertrain.
- In May 2015 Airbus announced that its new Airbus A350 XWB included over 1000 components manufactured by 3D printing.
- In 2015, a Royal Air Force Eurofighter Typhoon fighter jet flew with printed parts.
- The United States Air Force has begun to work with 3D printers, and the Israeli Air Force has also purchased a 3D printer to print spare parts.
- In 2017, GE Aviation revealed that it had used design for additive manufacturing to create a helicopter engine with 16 parts instead of 900, with great potential impact on reducing the complexity of supply chains. (Source: Wikipedia)
Some of the Pros of 3D Printing
Create Complex Designs
3D printing lets designers create complex shapes and parts – many of which cannot be produced by conventional manufacturing methods. By the natural laws of physics, manufacturing through additive methods means that complexity doesn’t have a price; elaborate product designs with complicated design features now cost just as much to produce as simple product designs that follow all the traditional rules of conventional manufacturing.
Customize each and every item
3D printing allows for easy customization – one only needs to change the design digitally to make changes with no additional tooling or other expensive manufacturing process required to produce the final product. Each and every item can be customized to meet a user’s specific needs without additional manufacturing costs.
No need for tools & moulds – lower fixed costs
Since 3D printing is a “single tool” process there is no need to change any aspect of the process and no additional costs or lead times are required between making an object complex or simple. Ultimately, this leads to substantially lower fixed costs.
Speed and ease of prototyping – faster and lower risk to market
Since there is no expensive tooling required to create objects through 3D printing, it is particularly a cost effective method for designers or entrepreneurs who are looking to do market testing or small production runs – or even launch their products through crowdfunding sites like Kickstarter. At this stage, it is also easy for design changes to be made without compromising more formal – and expensive – manufacturing orders. Thus, 3D printing offers a much less risky route to market for those who are looking into manufacturing a product idea.
Less Waste
Many conventional manufacturing processes are sub-tractive: you start with a block of material, cut it, machine it, and mill it until it has been processed as your intended design. For many products – such as a bracket for an airplane – it’s normal to lose 90% of the raw material during this process.
Alternatively, 3D printing is an additive process; you create an object from the raw material layer by layer. Naturally, when an object is manufactured this way, it only uses as much material that is needed to create that particular object. Additionally, most of these materials can be recycled and re-purposed into more 3D printed objects.
(Source: 3DHubs)
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
The most common technology for desktop 3D printing; great for quick and low-cost prototyping.